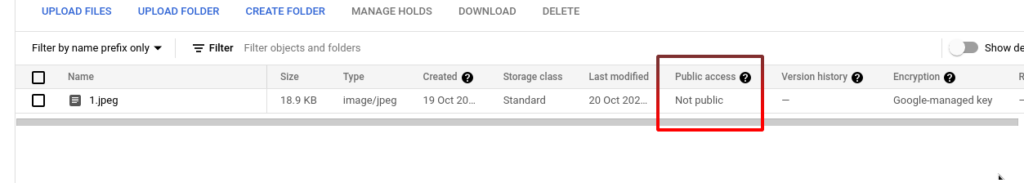
Squash two commits into one
Is it possible that you can’t use the visual squash commit with Github Desktop:
If the two commits is one before the other, so you can use the following command to take the 2 last commits :
git rebase -i HEAD~2
This will show the VI text editor, and you will have to change the text “pick” to “squash” for the last commit and only the last one because you only want the last to be squashed into the other one.
So, when you do this command, you will see something like:
pick abc1234567 Commit message for commit1
pick def1234567 Commit message for commit2
Change the second “pick” to “squash” :
pick abc1234567 Commit message for commit1
squash def1234567 Commit message for commit2
In VI editor, save it by pressing escape then: :x!
Do it another time if you can see another editor.
Check it with git log or Git Desktop
You can then force push to apply the changes and the remote repository.
git push --force
Squash several commits into one
To squash several commits, first you should know how many commits you want to squash.
If it is 15 commits, you should then you the following command:
git rebase -i HEAD~15
In the VI editor to search and replace “pick” to “squash” (with question that ask if you want to replace) use:
Press escape and then: :2,$s/pick/squash/c
⚠️ You should not replace the first one, the first one will still “pick”.
Then save it by pressing escape then: :x!
Here is an example, I did the rebase :
pick ab12345678 feat: important feature
pick cd12345678 feat: important feature to squash
pick ef12345678 feat: important feature to squash
pick gh12345678 feat: important feature to squash
Then I replace all the “pick” except the first one:
pick ab12345678 feat: important feature
squash cd12345678 feat: important feature to squash
squash ef12345678 feat: important feature to squash
squash gh12345678 feat: important feature to squash
# Rebase ab12345678..cd12345678 onto ef12345678 (2 commands)
#
# Commands:
# p, pick <commit> = use commit
# r, reword <commit> = use commit, but edit the commit message
# e, edit <commit> = use commit, but stop for amending
# s, squash <commit> = use commit, but meld into previous commit
# f, fixup [-C | -c] <commit> = like "squash" but keep only the previous
# commit's log message, unless -C is used, in which case
# keep only this commit's message; -c is same as -C but
# opens the editor
# x, exec <command> = run command (the rest of the line) using shell
# b, break = stop here (continue rebase later with 'git rebase --continue')
# d, drop <commit> = remove commit
:x!