React Native : fix ‘React/RCTDefines.h’ file not found
It is possible that after adding a new library in your React Native project (or after upgrading or adding some packages) you have the following error in XCode when you try to build:
<React/RCTDefines.h> file not found
or
'React/RCTDefines.h' file not found
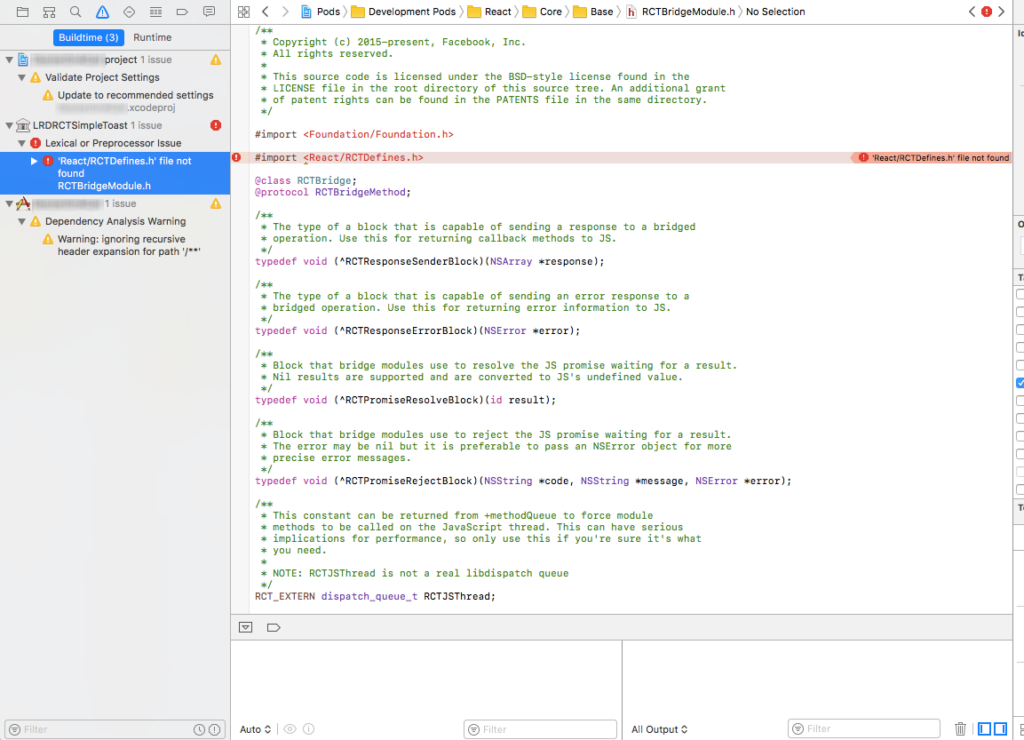
This error means that the library is not correctly set up with your React Native project.
To fix this error, go to your library settings. You will have to modify the Header Search Path input in Build Settings :
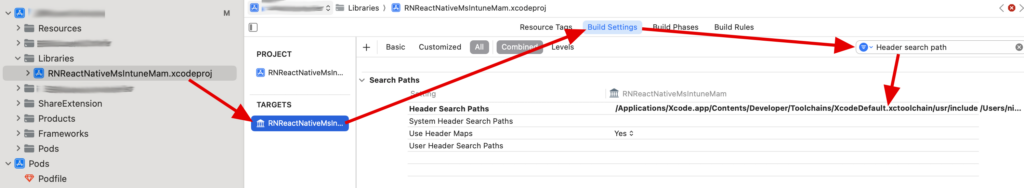
“Header Search Path” should be in the section “Search Paths”. I recommend to use the search input because there are a lot of fields.
In my case, the external library named “RNReactNativeMstuneMam.xcodeproj” was doing the problem, so I am opening the settings of the xcodeproj file of this project. It can be any other library with another name, but you will have to fix the xcodeproj file, following to the error path that you have.
Now, double click to Header Search Paths and add:
${SRCROOT}/../../../ios/Pods/Headers
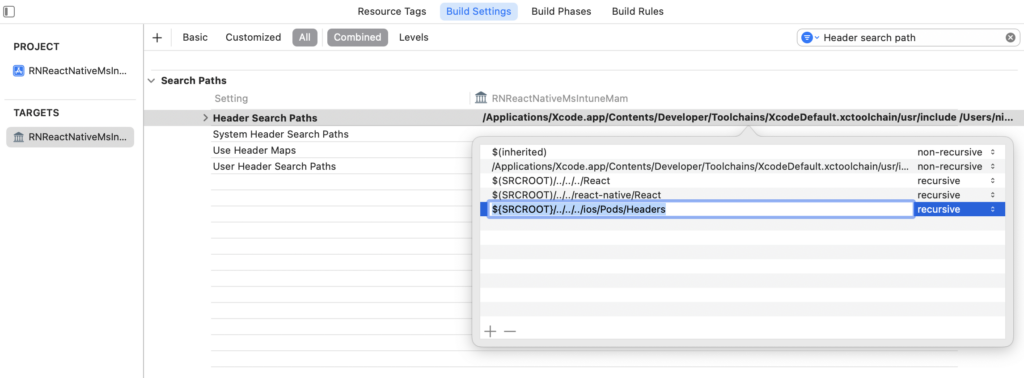
Set it to recursive:
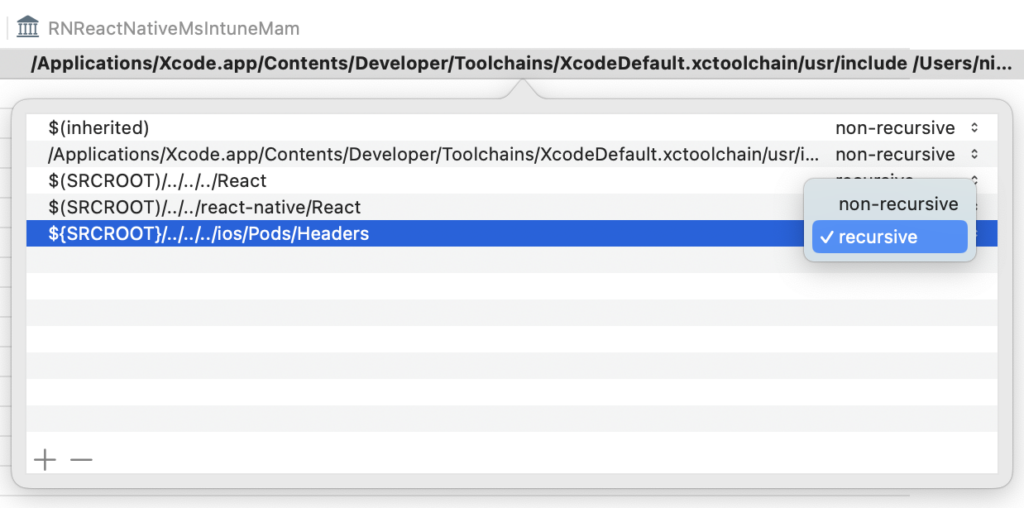
Now, you can clean and build again:
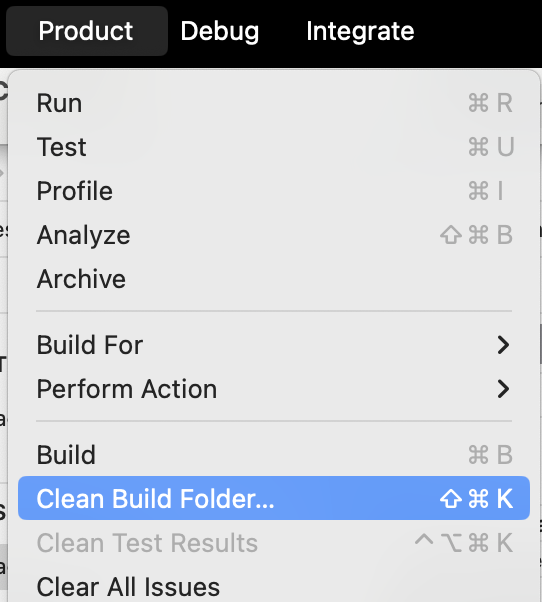
The error should not appear anymore as your library will find the Pods headers.