Import / Export MySQL Workbench tables in Google Cloud SQL database
If you have a database on Google Cloud and you want to import and export some tables to another database, you will need a database explorer to export your .SQL backup.
Export the tables you want in database
Google Cloud interface only allow to export all a database or a specific database, but not tables
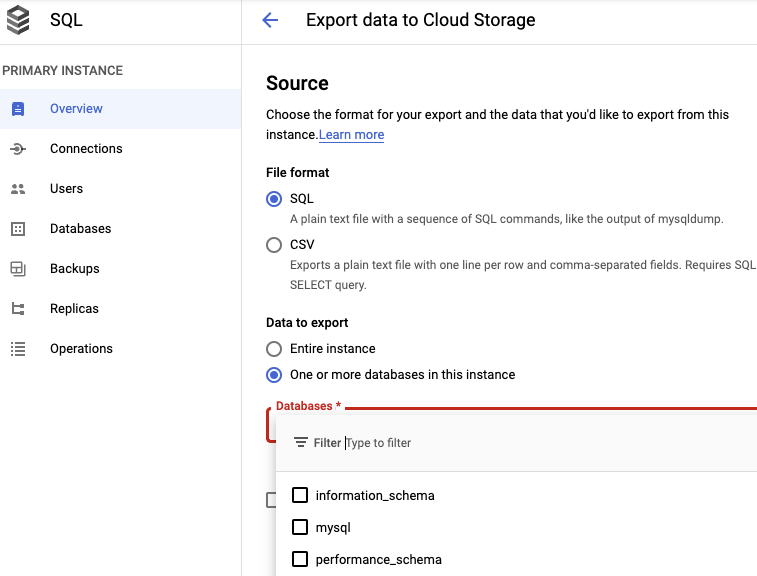
As you can see you don’t have the option to select tables.
To do so, you will have to connect the database with a SQL explorer.
In MySQL Workbench you should go in Server > Data Export
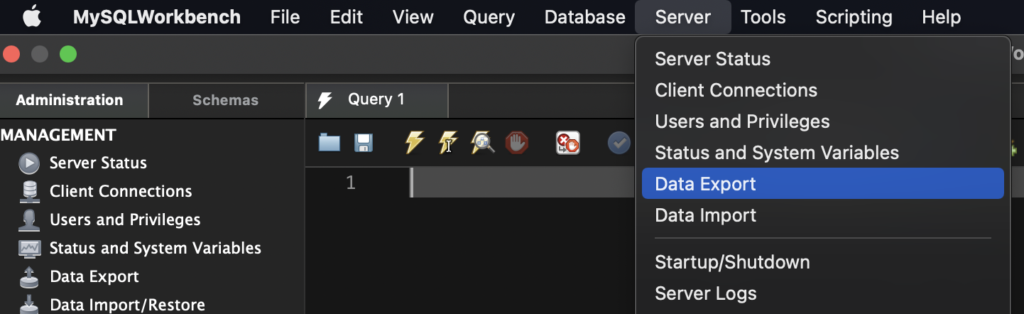
Then you should be able to select the tables you want
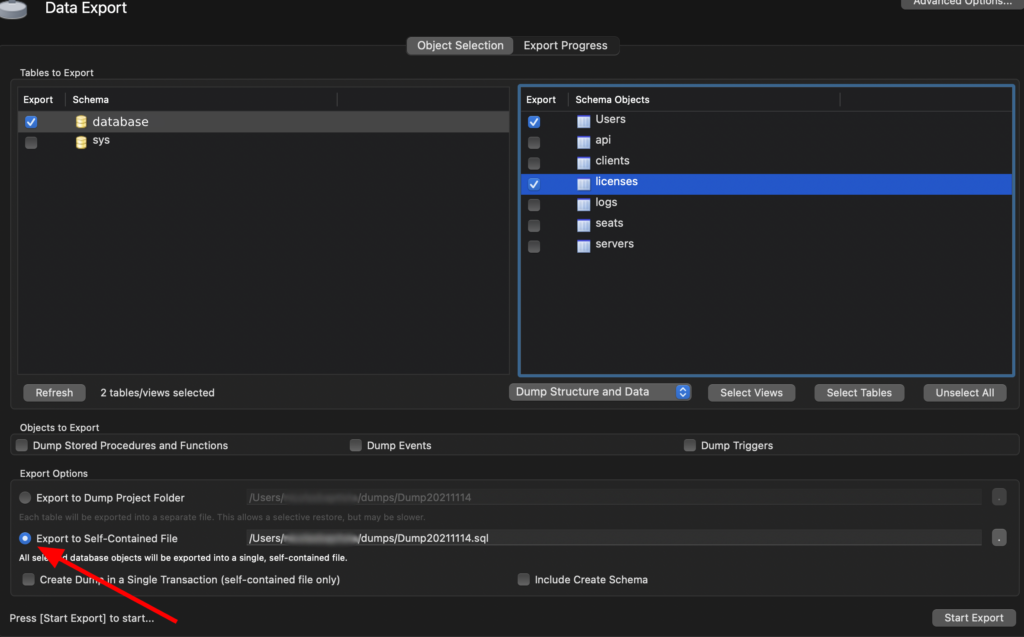
Import the SQL file to Google Cloud
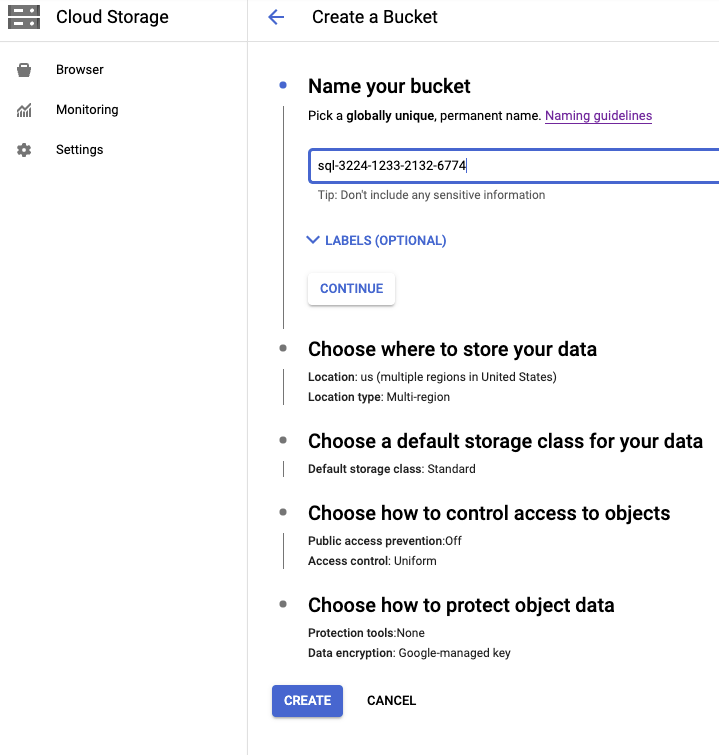
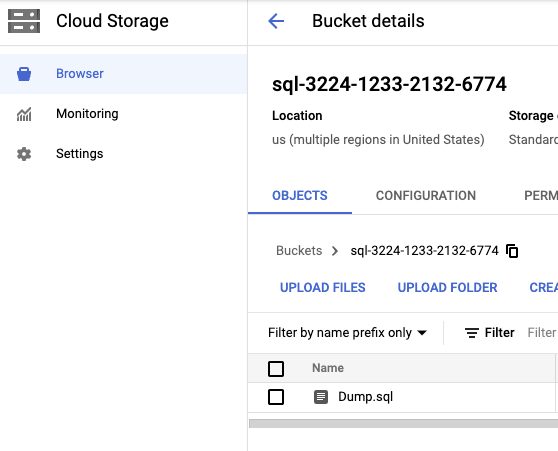
You will need to upload the SQL file to Google Cloud in order to import it. In order to do it, go to Google Cloud > Cloud Storage, create the bucket if it doesn’t exist yet :
Then, you can go on Google Cloud > SQL > Import
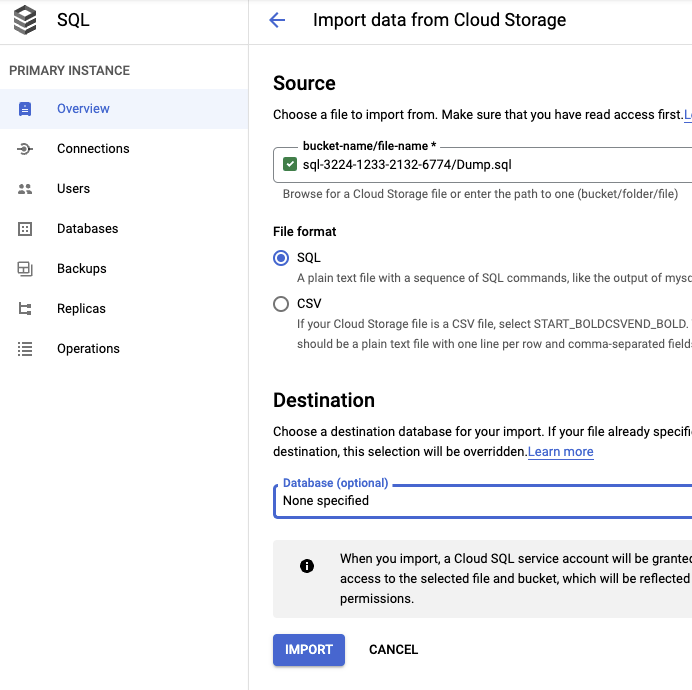
And then you should have imported successfully the tables on the selected database. You should check it in Operations
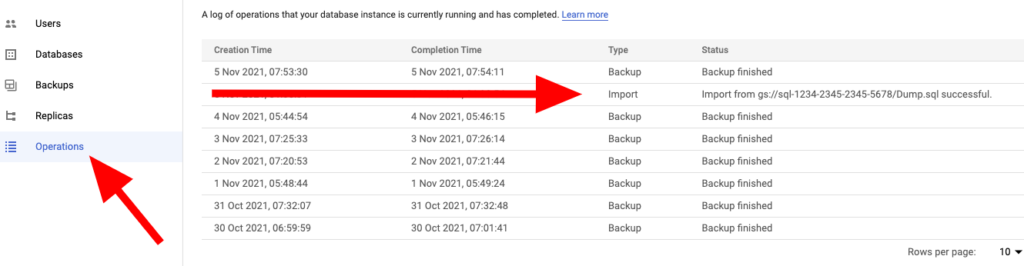
In case of errors, check the error in Operations, and modify the .SQL file with a text editor, search the error in the SQL file and remove the lines, and repeat the process (upload it again to Google Cloud Storage and import the SQL file again)